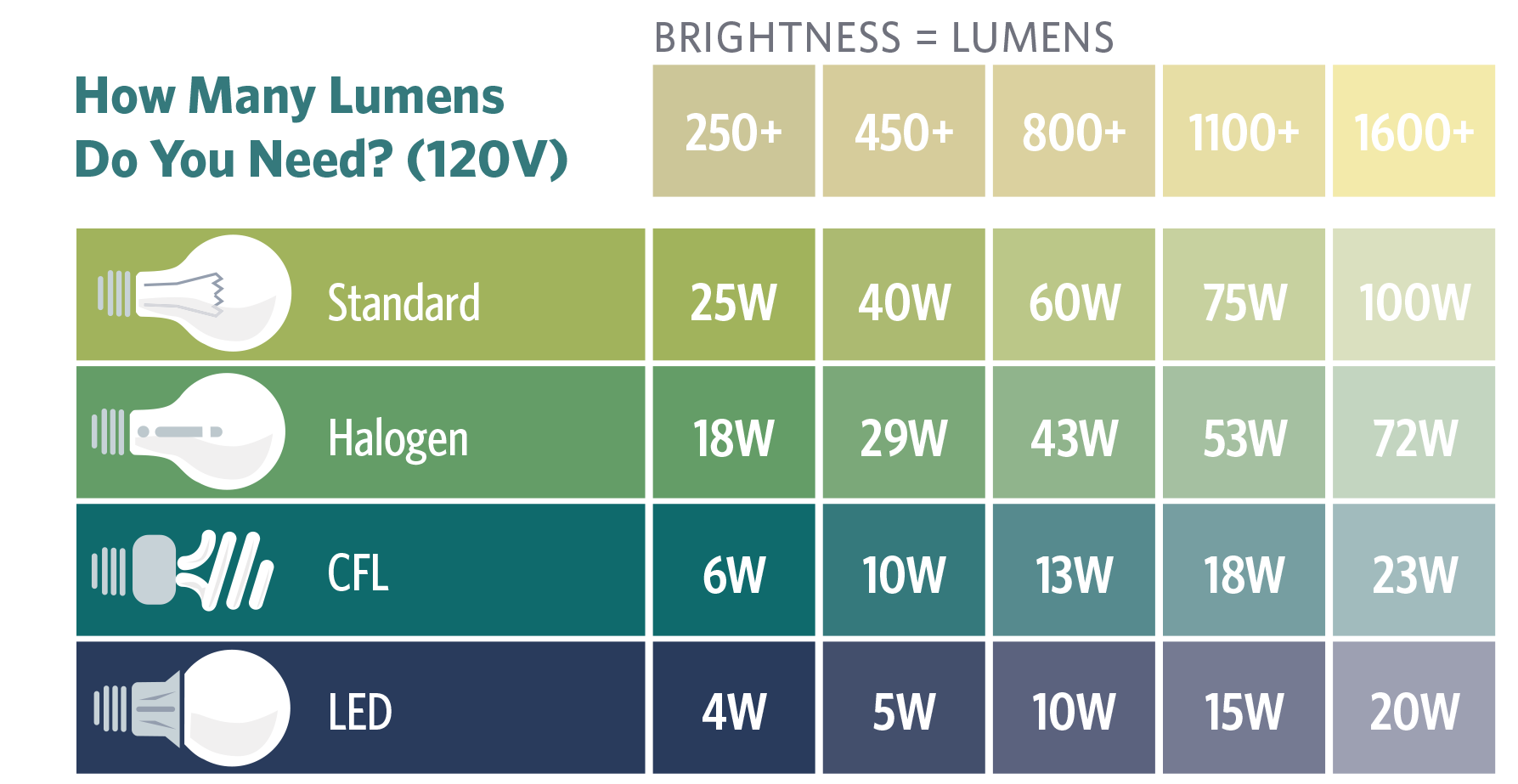
What is lumen?
Lumens are considered one of the most prominent units of measuring lighting, but what exactly is lumens? It is a unit that shows the amount of light present in a specific area. Each lumen is approximately equal to the light output of one candle. Basically, lumens are the measurement of brightness itself
One lumen equals 1.46 milliwatts and is equal to (1.46 x 10-3 watts) of radiated electromagnetic energy (EM) at a frequency of 540 terahertz or 5.40 x 1014 Hz. In short, in SI units, one lumen equals 0.00146 kilograms per square meter per second. Cubed 1.46 x 10-3 kg multiplied by meters squared/second squared.
Lumens are given the symbol lm and the flow of light is calculated internationally. One lumen has been defined as the amount of light shining from a solid angle of 1 lumen, through a source that radiates equally in all directions, and its intensity is 1 candela.

What is a watt and its equivalent?
Watts are a unit of measurement for energy consumption. By classic incandescent lighting, the higher the wattage, the brighter and more powerful the light. With energy efficient lighting such as LED, this varies somewhat because there is no hard and fast rule for relating wattage to output, for example One brand's 9 Watt LED bulb may shine enough lumens to replace a 60 Watt bulb, but another brand may want to use a lower lumen LED, so it's safe to say that 12 Watts is equivalent to creating enough lumens to replace a 60 Watt bulb.
Many household and commercial appliances are not designed to include LED bulbs because many do not take them into consideration. They usually include warnings that state “Equipment designed for max. A higher wattage bulb inside the device than it was intended for. LEDs consume much less electrical energy and, in turn, emit less energy. Therefore, a 60-watt LED bulb can be safely used in equipment designed for 40-watt lamps. The same applies to using a 60-watt LED bulb. With 75 watt devices designed for 60 watt incandescent.
The difference between lumens and watts
- The watt (W) is an international standard unit for electrical and mechanical energy to measure the rate of energy transfer. It can also be defined as one joule per second.
- It was given its name after the name of the Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer James Watt, who was born in 1736 and died in 1819, and was known for his work in the field of steam engine technology.
- All light bulbs are classified according to their wattage, and this is based on the fact that the higher the wattage, the higher the amount of electricity consumed or the electricity used, and thus the cost of lighting the light bulb increases.
- When incandescent bulbs dominated the lighting market, it was simple to determine how “powerful” the bulb was. Usually, a choice was made between 150 watts, 100 watts, 75 watts, 60 watts, and 40 watts. It was known that the higher the wattage, the higher the wattage. The light gets brighter.
- However, since new low-power lighting technologies, such as LED, CFL, and Halogen, have begun to compete with each other to become more efficient, the watt has become increasingly redundant as a true measure of the “brightness” of light.
- For example, a 60-watt bulb provides 42 halogen energy and an 11-watt CFL is considered equivalent to a 60-watt bulb known for similar levels of “luminance.” [4]
- To determine how “bright” a light bulb is, we must now resort to Lumens.